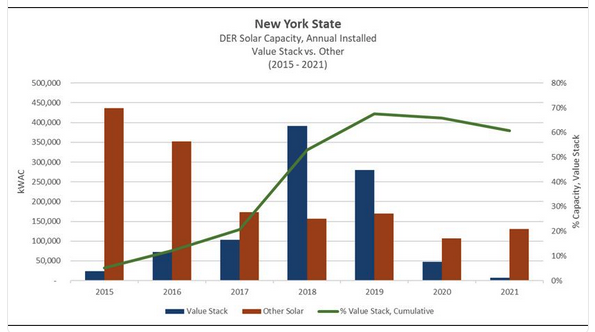
New York introduced the Value Stack as a compensation scheme designed to compensate distributed energy resources through multiple revenue streams, based on when and where they provide electricity to the grid. Compensation is in the form of monetary consideration for energy producers or bill credits for off-takers. The five components of value are energy, capacity, environmental, demand reduction and locational system relief. The Value Stack methodology applies to onsite nonresidential projects larger than 750 kilowatts AC and all remote-metered projects including those using a Community Distributed Generation (CDG) configuration
Value Stack capacity increased substantially during 2018 and 2019 as community solar projects were developed. 2020 and 2021 saw a sharp drop-off in Value Stack project completions as the New York market slowed with Covid-19 and supply chain issues.
With a current backlog of Value Stack projects exceeding 2,000 megawatts as of January 2022, we expect to see substantial growth in Value Stack capacity for the remainder of 2022 and into 2023.